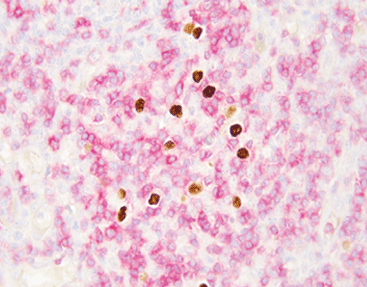
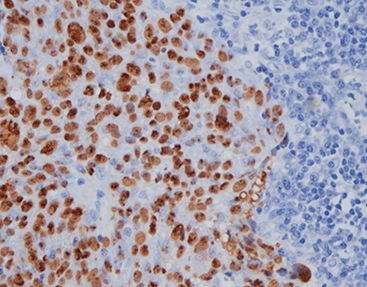
Is EBER the Same as EBV? Understanding the Key Differences

By admin
Introduction to EBV and EBER
What is Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) is a herpesvirus. It is a highly prevalent human virus that infects B lymphocytes and epithelial cells globally. It has the tendency to be latent in the host. EBV causes infectious mononucleosis. Most importantly, it is associated with malignancies like nasopharyngeal carcinoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, and gastric carcinoma. Its potential to go into latency and control host immune responses makes it of key importance to research in cancer studies and diagnostic pathology.
What is Epstein-Barr Encoded RNA (EBER)
Epstein-Barr Encoded RNAs (EBERs) are small non-coding RNA molecules. They are produced by the EBV genome in latent infections. They exist in abundance of molecules in infected cells—up to 10 million copies per cell. Experts identify them as good markers of EBV in tissue samples. Unlike viral proteins with variations by the latencies of dormancy, the EBERs exhibit uniform expression in all latent infections. Such consistency makes them excellent targets for diagnostic testing.
Relationship Between EBV and EBER
How EBER Relates to EBV Infection
EBERs signify dormant EBV infections in tissues. Their abundant transcription and nuclear retention provide stable molecular evidence of the virus. EBER detection doesn’t require active viral replication or protein expression. Consequently, pathologists identify EBV-related diseases even when other methods cannot detect low viral loads.
Why EBER Detection is Clinically Significant
Detecting EBER is essential for diagnosing numerous EBV-associated cancers. Since nearly all dormant infected cells express EBERs, they offer excellent sensitivity for confirming EBV involvement in tumors. Moreover, their nuclear position enables clear microscopic visualization using chromogenic or fluorescent probes.
Chromogenic in situ hybridization detects RNA. It employs the HRP-DAB chromogenic system to show staining outcomes under light microscopes. This technique ranks among pathology’s most practical molecular technologies. Its development delivers real clinical value. For example, EBER in situ hybridization now serves as the definitive standard for tissue-based EBV infection diagnosis.
Diagnostic Importance of EBER
Role of EBER in Pathological Diagnosis
In clinical pathology, identifying EBV involvement through EBER detection differentiates EBV-positive and EBV-negative tumor subtypes. This distinction influences treatment choices and outcome predictions. Certain lymphoma subtypes show better or worse prognoses depending on their EBV status.
Use of In Situ Hybridization for EBER Detection
In situ hybridization (ISH) remains the definitive method for EBER detection. It allows direct visualization within tissue structures. The technique uses labeled probes targeting EBER sequences in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples.
Enhanced chromogenic ISH delivers stronger signal intensity while preserving tissue structure. This makes it perfect for regular diagnostic applications.
Celnovte Products for EBER Detection
Celnovte ISH Probe: EBER/IHC Dual Staining Kit
Celnovte offers an advanced ISH probe kit. It enables simultaneous detection of EBER RNA and immunohistochemical markers on one slide. This approach simplifies diagnostics without sacrificing precision. The kit employs high-affinity probes with exceptional specificity. These ensure accurate localization even with low expression levels.
Dual-staining capability lets pathologists evaluate viral presence and cellular phenotypes concurrently. This proves particularly valuable when assessing tumor environments or distinguishing reactive from cancerous infiltrates.
Compatibility with Celnovte Automated Staining Systems
The dual-staining kit integrates smoothly with Celnovte’s fully automated immunohistochemistry systems. These processes can handle up to 60 slides per run within 2.5 hours.
They efficiently meet departmental automation requirements. Additionally, they support novel technologies like EBER chromogenic ISH, multicolor immunohistochemistry, and p16/Ki-67 dual staining. This makes them excellent platforms for contemporary pathology laboratories seeking efficiency without quality compromise.
Advantages of Celnovte’s EBER Detection Solutions
High Sensitivity and Specificity of Probes
Celnovte’s patented probe architecture provides enhanced binding specificity with minimal background interference. This facilitates strong signal-to-noise ratios in sparse target conditions.
Repeat comparisons confirm the benefit. The kits yield stronger signals, signal-to-noise ratio increases, and reliable biomarker localization. These are critical when detecting low-copy targets like viral RNAs during nascent disease or post-treatment evaluation.
Streamlined Workflow and Reduced Turnaround Time
Combining ISH with IHC on single slides via automated platforms reduces labor intensity. Simultaneously, it improves result consistency across cases.
Our careful protocol design minimizes deviations from established systems. Laboratories can therefore adopt our solutions with negligible workflow interruptions. They also gain faster processing times.
Clinical Applications of EBER Testing
Diagnosing EBV-Associated Malignancies
EBER testing is indispensable for diagnosing several cancers, including:
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Hodgkin lymphoma
- Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma
- Gastric carcinoma
These diagnoses frequently require EBV confirmation through tissue-based assays. Validated probe kits like Celnovte’s serve this purpose effectively.
Monitoring Disease Progression and Treatment Response
EBER expression patterns may shift over time or post-treatment. Repeat testing, therefore, helps evaluate therapy effectiveness and detect recurrences early. This provides actionable insights throughout patient management.
Choosing the Right Tools for Your Lab
Selecting the Right Probe Kit for Your Needs
When choosing an ISH kit for EBER detection, consider:
- Sensitivity requirements
- Compatibility with existing workflows
- Probe stability in FFPE conditions
- Operational simplicity
Celnovte products excel in all areas. Rigorous GMP-compliant manufacturing ensures quality. The parent company holds ISO9001, ISO13485, and EU CE-ID certifications. This places its product line at industry-leading quality levels.
Ensuring Compatibility with Existing Lab Equipment
Celnovte’s kits prioritize flexibility. They work fully with manual protocols and automated platforms like Leica Bond RX or Ventana BenchMark systems. This versatility suits laboratories at any automation level.
FAQ
Q: Is EBER testing necessary with known EBV infection?
A: Yes. Serological tests only confirm systemic infection history. Tissue-based EBER detection proves active dormant infection at cancer-relevant anatomical sites.
Q: Can Celnovte’s dual-staining kit work on old FFPE blocks?
A: Yes. Probes work effectively on FFPE samples after extended storage. However, proper antigen retrieval protocols remain essential for the best results.
Q: How does Celnovte’s performance compare to competitors?
A: Comparative data show stronger signal intensities versus alternatives. This makes Celnovte optimal for high-resolution imaging and multiplexed diagnostics involving EBER.
Q: Does your automated system require special training?
A: No additional training is needed beyond standard histopathology practices. Systems include intuitive interfaces with comprehensive manuals and customer support via info@celnovte.com or shop.celnovte.com.
RELATED PRODUCTS