EBER Detection in Medical Testing: What You Need to Know
2026-02-20
By admin
In the detailed field of clinical diagnostics, spotting viral causes of cancer remains a central task for pathologists. One key marker stands out: EBER, short for Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs. Although Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) ranks among the most widespread human viruses, its involvement in several lymphomas and carcinomas calls for tests that are highly accurate. For pathologists and oncologists, grasping EBER goes beyond finding a virus. It often provides the clear evidence needed to confirm serious diagnoses that change patients’ lives.
Celnovte, a trusted maker of advanced pathology reagents and equipment, supplies the reliable tools that reveal these molecular clues with sharp detail.
Understanding EBER in Medical Terms
What are EBERs and Why Do They Matter
EBERs consist of non-coding RNAs made by the Epstein-Barr virus while it stays in its quiet, latent stage. These molecules appear in the highest numbers among all viral products inside infected cells—often reaching 107 copies in a single cell. Since almost every EBV-related cancer shows steady EBER expression, they make an excellent target for testing. Viral proteins can come and go, but EBERs stay present and stable. That consistency gives a dependable sign of the virus inside the cell nucleus.
The Clinical Connection: EBV-Associated Pathologies
EBER testing carries weight across different areas of cancer medicine. EBV links closely to several conditions, among them Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma (NPC), Hodgkin Lymphoma, Burkitt Lymphoma, and various NK/T-cell lymphomas. In many biopsy samples, a positive EBER result settles whether the changes represent a reactive process or true malignancy. For example, in some gastric cancers, finding EBER points to a separate molecular type that carries its own outlook and treatment considerations.
EBER In-Situ Hybridization (ISH): The Diagnostic Gold Standard
Why ISH Overcomes Traditional Testing Limitations
Blood tests or PCR methods can show EBV in circulation, yet they fall short when the task is to prove the virus drives changes in a particular tissue. In-situ hybridization (ISH) holds the position of the preferred method for confirming EBV in tissue samples. Labeled probes attach straight to EBER sequences inside preserved cells. This approach lets pathologists observe precisely which cells carry the virus while keeping the normal layout of the tissue intact.
Visualizing Viral Latency under the Microscope
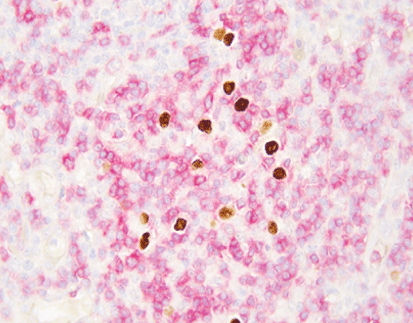
The strength of EBER ISH shows clearly in the stained images. Positive signals form distinct dark deposits—usually from a DAB chromogen—inside the nuclei of affected cells. Pathologists then judge viral presence against the surrounding cell types. They can separate true infection in tumor cells from harmless EBV in nearby bystander lymphocytes.
Celnovte Solutions: Precision in EBER Detection
The Celnovte EBER Probe: Single-Molecule Sensitivity with Super-ISH™ Technology
The core of Celnovte’s molecular offerings is the high-performing EBER Probe. It meets the strict needs of busy clinical labs. This probe builds on the company’s Super-ISH™ RNA In-Situ Hybridization Technology, which brings clear gains in both sensitivity and clarity.
Key Features and Advantages:
- Single-Molecule Resolution: The Super-ISH™ system detects RNA targets down to individual molecules. Even infections with very few copies do not escape notice.
- Superior Signal-to-Noise Ratio: Careful design cuts down unwanted background color. Slides stay clean and straightforward to read.
- Compatibility: The probe works smoothly with the standard HRP-DAB chromogenic method. Results appear clearly under an ordinary light microscope—no fluorescence equipment required.
EBER/CD20 Dual Staining Kit: Redefining Multiplex Diagnostics
In difficult cases, simply confirming EBER is not enough. Pathologists also need to know the cell type that harbors the virus. Celnovte’s EBER/CD20 Dual Staining Kit combines molecular ISH and immunohistochemistry (IHC) on the same slide.
Key Features and Advantages:
- Simultaneous Detection: The kit shows EBER (proof of EBV) and CD20 (a standard B-cell marker) at the same time.
- Tissue Conservation: Running both tests on one slide preserves limited material—especially helpful for tiny needle biopsies or samples from children.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Viewing both markers together removes the need to match separate slides. This avoids mismatches caused by timing or position.
- Clearer Localization: Different chromogens highlight the exact position of the virus and cell type. That makes disease classification more straightforward.
The Celnovte Advantage: Quality, Innovation, and Automation
Celnovte began operations in 2010. The company concentrates on creating and producing high-quality pathology reagents with a focus on improving cancer diagnosis accuracy. Manufacturing sites follow NMPA and GMP rules. Certifications include ISO13485, ISO9001, FDA registration, and CE IVDR.
Standardizing Workflows with the CNT 360 Full Automatic Stainer
Reliable EBER results depend on consistent handling. Celnovte’s CNT 360 Full Automatic IHC & ISH Stainer handles the full process. It automates probe binding and signal development steps. Labs gain uniform staining quality and shorter turnaround times. Automation lowers the chance of mistakes and supports busy departments that process many samples each day.
A Global Commitment to Diagnostic Excellence
Celnovte products undergo thorough checking. Self-developed primary antibodies and detection systems have earned “optimal” or “good” ratings in NordiQC proficiency surveys for several years running. More than 1000 CNT 360 stainers operate worldwide. The network covers over 2300 leading hospitals in China and extends to more than 40 countries.
Conclusion: Elevating the Future of Molecular Pathology
Precision medicine grows more important each year. Accurate EBER detection plays a larger role in that progress. Celnovte continues to supply pathologists with forward-looking tools, from the single-molecule detail of the Super-ISH™ EBER Probe to the practical advantages of the EBER/CD20 Dual Staining Kit. Through steady focus on quality, scientific care, and efficient automation, the company works to help every patient receive diagnoses that are both correct and prompt.
FAQ
Q: Why is EBER considered more reliable than IHC for detecting EBV?
A: EBERs appear in large, steady amounts during viral latency. Viral proteins such as LMP1 show up less consistently. For that reason, ISH targeting EBER proves more sensitive than IHC when confirming EBV in tissue.
Q: Can the EBER/CD20 Dual Staining Kit be used on frozen sections?
A: Celnovte offers PolyStacker™ technology for rapid 10-minute IHC on frozen tissue. However, EBER/CD20 dual staining works best on paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples to preserve the strongest signals.
Q: Does the CNT 360 stainer support both IHC and EBER ISH?
A: Yes. The CNT 360 handles both IHC and ISH protocols on the same platform. It delivers high-volume processing and a smooth laboratory routine.
Q: Are Celnovte’s EBER probes compatible with standard light microscopes?
A: Yes. The probes rely on a chromogenic (CISH) detection method. Pathologists view clear results using a regular light microscope—no fluorescence setup needed.