Kappa vs. Lambda Light Chains: Key Differences and Their Role in Antibody Production
2025-04-15
By admin
Antibodies are the overlooked champions of our immune system. They relentlessly shield us from infections and illnesses. Central to these mighty proteins are light chains, namely Kappa and Lambda Light Chains, which perform a vital function in antibody composition and effectiveness. If you’ve ever pondered the variances between these two light chain types or their significance in tests like the kappa blood test, you’ve landed in the perfect spot. This article delivers a straightforward, brief, and informative overview of kappa and lambda light chains, their distinct traits, and their crucial roles in antibody creation. Whether you’re a learner, a medical expert, or just intrigued by immunology, let’s plunge into this captivating subject.
What Are Light Chains in Antibodies?
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are Y-shaped molecules crafted by plasma cells. These cells are a variety of white blood cells stemming from B cells. Each antibody comprises two heavy chains and two light chains. These components connect to form a working unit adept at identifying and neutralizing invaders. The light chains exist in two forms: kappa (κ) and lambda (λ). They aren’t merely building blocks. Instead, they boost the variety and precision of antibodies. This enables the immune system to combat a wide range of dangers.
Light chains are fairly tiny proteins, weighing around 25 kDa. They team up with heavy chains (such as IgG, IgA, or IgM) to construct the full antibody. Heavy chains determine the antibody’s category, but light chains enhance its ability to latch onto antigens. In robust individuals, kappa and lambda light chains coexist in the bloodstream. They maintain a steady proportion that mirrors typical immune activity.
Kappa vs. Lambda Light Chains: Key Structural Differences
Grasping the contrasts between kappa and lambda light chains begins with their makeup. Though both fulfill comparable tasks in antibodies, their genetic roots and physical qualities distinguish them.
Genetic Origins
- Kappa Light Chains: These are encoded by genes on chromosome 2. They emerge from a lone site with numerous variable (V) and joining (J) gene pieces. This setup permits substantial diversity via recombination.
- Lambda Light Chains: These arise from genes on chromosome 22. They stem from several sites, providing a unique recombination process. Humans possess various lambda subtypes (λ1, λ2, λ3, and so on). This adds intricacy to their genetic structure.
Molecular Structure
- Kappa: Usually appears as a monomer (a solitary unit). This makes it lighter. Consequently, the kidneys filter it more readily.
- Lambda: Frequently forms dimers (two units joined together). This impacts its removal speed and steadiness in the blood.
Here’s a swift comparison:
|
Feature |
Kappa Light Chains |
Lambda Light Chains |
|
Chromosome |
2 |
22 |
|
Structure |
Monomeric |
Dimeric |
|
Gene Segments |
Single locus (V, J) |
Multiple loci (V, J, C) |
|
Subtypes |
One type |
Multiple (λ1, λ2, etc.) |
These structural disparities affect how kappa and lambda light chains operate in the body. They also influence their detection in assessments like the kappa blood test.
Functional Roles in Antibody Production
Both kappa and lambda light chains are essential to antibody formation. However, their roles vary slightly due to their physical attributes.
Antigen Binding
The variable areas of light chains pair with those of heavy chains. Together, they create the antigen-binding spot. Kappa and lambda chains contribute equally here. They allow antibodies to pinpoint specific threats. The diversity from their genetic mixing ensures a wide-ranging immune reaction.
Production Balance
In fit individuals, plasma cells generate more kappa than lambda light chains. The usual kappa-to-lambda ratio in serum is about 2:1. Yet, this equilibrium shifts in certain ailments. That’s why measuring free light chains through a kappa blood test or lambda test is a helpful diagnostic method.
Free Light Chains
Not every light chain links to a heavy chain. Surplus “free” light chains (FLCs) float in the blood. The kidneys filter them out. Kappa FLCs, being monomeric, exit faster than dimeric lambda FLCs. This difference alters their measurable levels in diagnostic evaluations.
Diagnostic Importance: Kappa Blood Test and Beyond
The kappa blood test and lambda light chain assessments are pivotal in identifying and tracking conditions tied to irregular antibody output. This is especially true for plasma cell issues like multiple myeloma.
Why Test Kappa and Lambda Levels?
In disorders like multiple myeloma, plasma cells overproduce one light chain type—either kappa or lambda. This disrupts the usual ratio. A kappa blood test gauges free kappa light chains in serum. A parallel test checks lambda levels. The kappa-to-lambda ratio (normal range: 0.26–1.65) offers clues about immune wellness.
- Elevated Kappa Levels: These might suggest kappa-type multiple myeloma or other monoclonal gammopathies.
- Elevated Lambda Levels: These point to lambda-type conditions.
- Unusual Ratio: This indicates possible disease advancement or recovery.
For a closer look at diagnostic aids, explore Celnovte’s Kappa Light Chain reagents, crafted for accurate measurement.
Applications in Research and Medicine
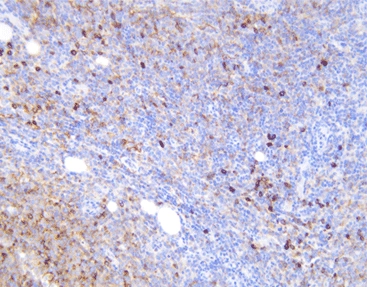
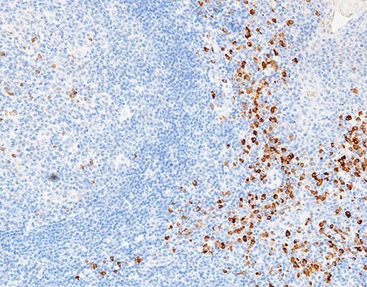
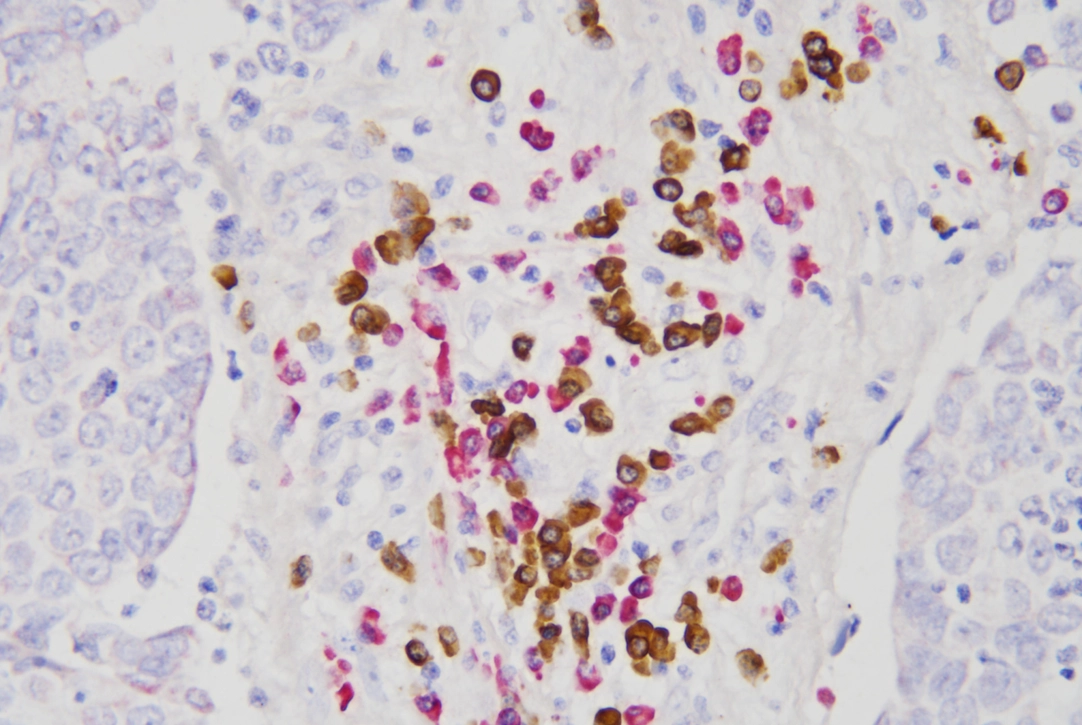
Beyond diagnostics, kappa and lambda light chains are examined in immunology studies. Researchers aim to comprehend immune reactions and devise precise treatments. Tools like the Kappa/Lambda Probe Kit (ISH) let scientists observe these chains in tissue samples. This advances our grasp of antibody behavior.
Celnovte: Your Trusted Antibody Supplier
Before we conclude, let’s highlight Celnovte, a frontrunner in antibody-related offerings. Located in Suzhou, China, with a worldwide presence, Celnovte excels in innovative diagnostic reagents and gear. From Kappa Light Chain probes to molecular diagnostic instruments in their molecular section, Celnovte equips medical experts and scientists with top-notch products. Visit [Celnovte’s homepage](insert link here) to discover their groundbreaking solutions and dedication to enhancing clinical diagnostics.
FAQs: Kappa vs. Lambda Light Chains
Q1. What’s the primary distinction between kappa and lambda light chains?
A1. Kappa light chains come from chromosome 2 and are monomeric. In contrast, lambda light chains, from chromosome 22, often form dimers and have several subtypes. Both aid antibody tasks but differ in structure and clearance pace.
Q2. Why is a kappa blood test significant?
A2. A kappa blood test measures free kappa light chains in the blood. It detects imbalances tied to conditions like multiple myeloma. It assists doctors in diagnosing and tracking plasma cell disorders by evaluating the kappa-to-lambda ratio.
Q3. Can you have both kappa and lambda in one antibody?
A3. No, each antibody has either two kappa or two lambda light chains, not both. This exclusivity occurs during B-cell growth. It ensures a consistent light chain type per antibody.
Q4. How are kappa and lambda levels gauged?
A4. Levels are assessed using immunoassays, like the serum free light chain (SFLC) assay. This often involves a kappa blood test or lambda test. These exams measure free light chains and compute their ratio for diagnostic use.
Take the Next Step in Understanding Immunology
Kappa and lambda light chains might appear as minor actors in the vast realm of immunity. Yet, their distinctions and roles in antibody creation are significant. Whether you’re delving into the science of a kappa blood test or aiming to expand your immunology knowledge, this overview provides a firm base. Ready to explore further or access advanced tools? Visit Celnovte’s homepage for resources and products that bring accuracy to antibody research and diagnostics. Immerse yourself in the realm of light chains and enrich your understanding today!